Atlas of Crystals found in acidic urine, Sulfonamide crystals, Bilirubin crystals, granular cast, X-ray dye crystals, Cholesterol crystals, Tyrosine crystals, Leucine crystals, Cystine crystal, Hippuric acid crystals, Calcium oxalates, amorphous urate, amorphous urates, Uric acid, Sodium urate crystals, Uric acid crystal, atlas in medical, tuyenlab.net
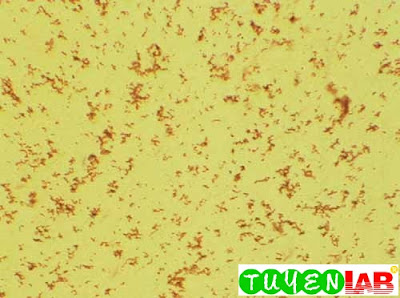 |
| Figure 21. Amorphous urates (100x) |
 |
| Figure 22. Amorphous urates. The urates in this field are clumped close together. Note the characteristic color (100x) |
 |
| Figure 23. Uric acid crystals, diamond or rhombic form. These crystals are very thin and almost colorless (400x) |
 |
| Figure 24. Uric acid crystals in the urine of a patient with a kidney stone. Note the heavy clumps of crystals that were present, even in the fresh specimen (400x) |
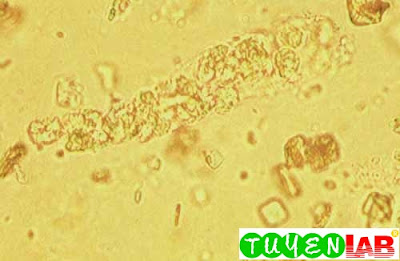 |
| Figure 25. WBC cast and uric acid crystals. Same patient as in previous figure (400x) |
 |
| Figure 26. Uric acid crystals in rosette formation (400x). |
 |
| Figure 27. Uric acid crystals, atypical form (400 ) |
 |
| Figure 28. Uric acid crystals, layered formation (500x). |
 |
| Figure 29. Uric acid crystals, thick rosette formation (200x) |
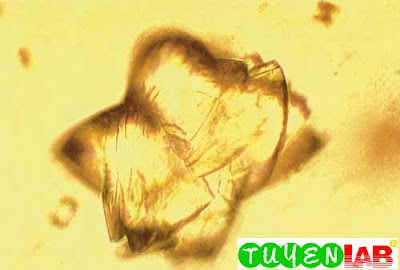 |
| Figure 30. Uric acid, thick rosette formation under higher power. Note the many layered crystals (500x). |
 |
| Figure 31. Uric acid and calcium oxalate crystals (500x) |
 |
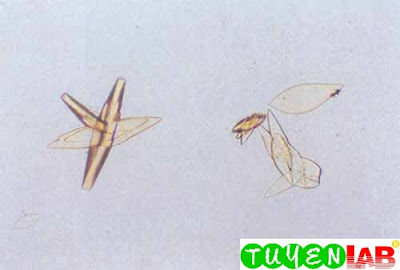
| Figure 32. Uric acid crystals under polarized light. Note the small crystal (400x) |
 |
| Figure 33. Uric acid under polarized light (400x). |
 |
| Figure 34. Uric acid crystals (100x) |
 |
| Figure 35. Uric acid crystals under polarized light (100x) |
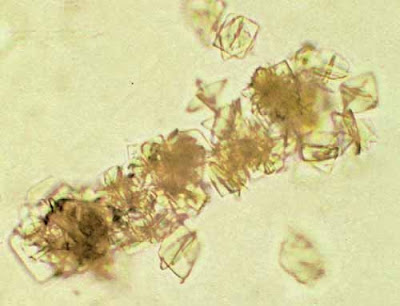 |
| Figure 36. Uric acid crystals in pseudocast formation (400x) |
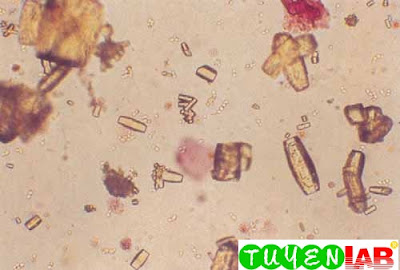 |
| Figure 37. Uric acid, barrel shape, and yeast in the background (200x) |
 |
| Figure 38. Sodium urate crystals. Note the square ends on each needlelike crystal (400x) |
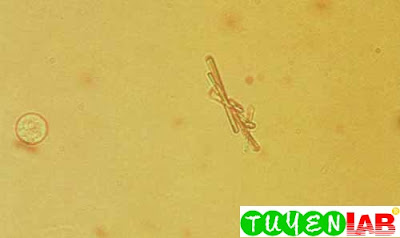 |
| Figure 39. Sodium urates and a WBC. Notice how narrow these crystals are (400x) |
 |
| Figure 40. Sodium urate crystals |
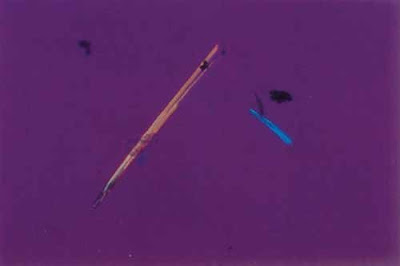 |
| Figure 41. Uric acid, needle shape under polarized light with red compensator (400x ) |
 |
| Figure 42. Calcium oxalate crystals (200x) |
 |
| Figure 43. Calcium oxalate crystals. Even under low power magnification, the characteristics of the crystals are easily recognized (160x) |
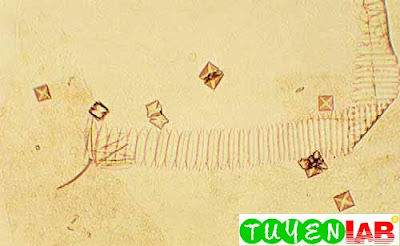 |
| Figure 44. Calcium oxalates, amorphous urates, and a piece of debris. Some of the crystals cracked when the coverslip was touched (200x ). |
 |
| Figure 45. Calcium oxalate crystals clustered around a piece of debris. The field also contains squamous epithelial cells as well at many calcium oxalates (100x) |
 |
| Figure 46. Calcium oxalates and amorphous urates (100x) |
 |
| Figure 47. Hippuric acid crystals (400x) |
 |
| Figure 48. Cystine crystals (160x) |
 |
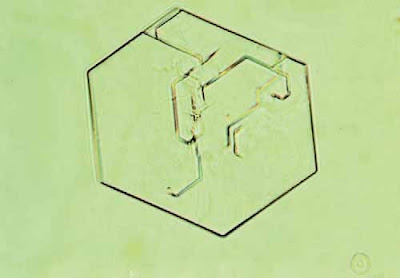
| Figure 49. Cystine crystal with unequal sides (1000x) |
 |
| . Figure 50. Cystine crystals. Note how these crystals can form clusters (160x) |
 |
| Figure 51. Cystine crystal with layered or laminated surface (1000x) |
 |
| Figure 52. Cystine crystals and a squamous epithelial cell. Some crystals have laminated surfaces and others are quite thick. The arrow shows a thick crystal that is turned on its edge (400x) |
 |
| Figure 53. Leucine crystals. Note what appears to be a thick double wall and a striated center |
 |
| Figure 54. Leucine crystals under interference contrast microscopy. |
 |
| Figure 6-55. Tyrosine crystals. Note how black the crystals appear on low power (160x) |
 |
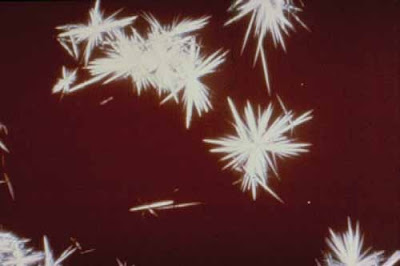
| Figure 56. Tyrosine crystals. Note the fine, very pointy needles (1000x). |
 |
| Figure 57. Tyrosine crystals (1000x). |
 |
| Figure 58. Tyrosine crystals under polarized light |
 |
| Figure 59. Tyrosine crystals (1000x) |
 |
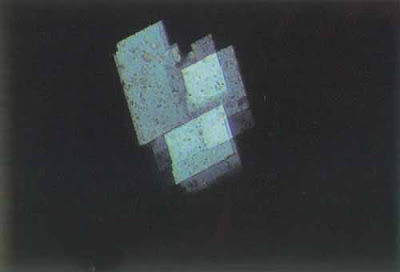
| Figure 60. Cholesterol crystals from “kidney fluid” (200x) |
 |
| Figure 61. Same specimen as the previous figure under polarized light. |
 |
| Figure 62. X-ray dye crystals. Specific gravity of the specimen was 1.070 (160 ). |
 |
| Figure 63. X-ray dye crystals (400x) |
 |
| Figure 64. X-ray dye crystals under polarized light (160x) |
 |
| Figure 65. Bilirubin crystals and bilirubin-stained WBC and granular cast (500x). |
 |
| Figure 66. Bilirubin crystals and bilirubin-stained sediment (500x) |
 |
| Figure 67. Bilirubin crystals. |
 |
| Figure 68. Sulfonamide crystals (400x ) |
 |
| Figure 69. Sulfonamide crystals under polarized light with red compensator. |
This is only a part of the book : Graff's Textbook of Urinalysis and Body Fluids Second Edition of authors: Lillian A. Mundt and Kristy Shanahan. If you want to view the full content of the book and support author. Please buy it here: https://goo.gl/Kxf9i1










COMMENTS