Atlas of Diagnostic Parasitology, Diagnostic Parasitology, Generalized life cycle of intestinal ameba., Entamoeba histolytica , Entamoeba hartmanni , Endolimax nana, Iodamoeba bütschlii, Naegleria fowleri, Giardia lamblia, Dientamoeba fragilis, Chilomastix mesnili, Life cycle of Leishmania spp, Life cycle of Trypanosoma cruzi, Life cycle stages of malaria, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium falciparum, Toxoplasma gondii, Cryptosporidium, Life cycle of liver, lung, and intestinal flukes., Fasciola hepatica/Fasciolopsis buski, Paragonimus westermani, Diagram of a tapeworm., Life cycle of Taenia spp, Hymenolepis
 |
| Fig 1. Relationship of stool consistency to protozoan stage. |
 |
| Fig 2. Generalized life cycle of intestinal ameba. |
 |
| Fig 3. A, Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite (trichrome stain). B, E. histolytica trophozoite. Notice darkly staining, ingested red blood cell near the nucleus (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 4. Entamoeba histolytica cyst with round-end chromatoidal bars. Two nuclei are visible (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 5.
A, Entamoeba hartmanni (trichrome stain). B, Enlarged view of E. hartmanni. |
 |
| Fig 6. Entamoeba hartmanni cyst (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 7. A, Entamoeba coli trophozoite. Notice dark staining, highly vacuolated cytoplasm (trichrome stain). B, Enlarged view of E. coli trophozoite to demonstrate peripheral chromatin (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 8. A, Entamoeba coli cyst (merthiolate-iodine-formalin) wet mount. B, E. coli cyst with five nuclei visible (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 9. Endolimax nana trophozoite (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 10.
A, Endolimax nana cyst (trichrome stain). B, Enlarged view of E. nana cyst (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 11. Iodamoeba bütschlii trophozoite (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 12. Iodamoeba bütschlii cyst with prominent glycogen vacuole (iron hematoxylin stain). |
 |
| Fig 13. Blastocystis hominis vacuolar form (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 14. Naegleria fowleri trophozoite. Note prominent karyosome (iron hematoxylin stain). |
 |
| Fig 15.
A, Balantidium coli trophozoite. Arrow denotes the cytostome (trichrome stain). B, B. coli cyst (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 16. Generalized life cycle for intestinal flagellates. |
 |
| Fig 17.
A, Giardia lamblia trophozoite (trichrome stain). B, Enlarged view of G. lamblia trophozoite (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 18. Giardia lamblia cysts (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 19. Dientamoeba fragilis binucleate trophozoite (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 20. Chilomastix mesnili cyst (trichrome stain). |
 |
| Fig 21. Life cycle stages of the blood and tissue flagellates. |
 |
| Fig 22. Life cycle of Leishmania spp. |
 |
| Fig 23. Amastigotes of Leishmania spp. |
 |
| Fig 24. Life cycle of the agents of sleeping sickness (Trypanosoma bruceigambiense and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense). |
 |
| Fig 25. Trypanosoma trypomastigote in a blood smear. |
 |
| Fig 26. Life cycle of Trypanosoma cruzi. |
 |
| Fig 27. Life cycle of Plasmodium spp. |
 |
| Fig 28. Life cycle stages of malaria. |
 |
| Fig 29.
A, Plasmodium vivax trophozoite. B, P. vivax mature schizont. C, P. vivaxmacrogametocyte. D, P. vivax microgametocyte. |
 |
| Fig 30. A, Plasmodium malariae band form trophozoite. B, P. malariae schizont. |
 |
| Fig 31. A, Plasmodium ovale trophozoite. B, Schüffner’s stippling of P. ovale clearly visible. |
 |
| Fig 32. A, Plasmodium falciparum ring-form trophozoites. B, P. falciparum gametocyte. |
 |
| Fig 33. A, Babesia microti trophozoite. B, B. microti tetrad form |
 |
| Fig 34. A, Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. B, T. gondii tachyzoites in lung tissue. |
 |
| Fig 35. Life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii. |
 |
| Fig 36. Life cycle of Cryptosporidium sp. |
 |
| Fig 37. Cryptosporidium oocysts (modified acid-fast stain). |
 |
| Fig 38. Isospora belli oocysts (modified acid-fast stain). |
 |
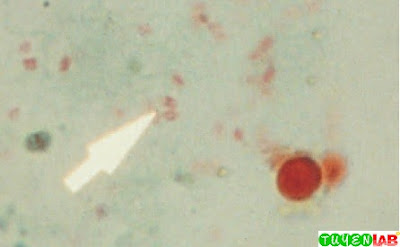
| Fig 39.
Cyclospora cayetanensis oocyst. A, Wet mount. B, Modified acid-fast stain. |
 |
| Fig 40. Microsporidia spores (chromotrope stain). |
 |
| Fig 41. Life cycle of liver, lung, and intestinal flukes. |
 |
| Fig 42. Fasciola hepatica/Fasciolopsis buski egg. |
 |
| Fig 43. Clonorchis sinensis egg. |
 |
| Fig 44. Paragonimus westermani egg. |
 |
| Fig 45. Life cycle of blood flukes (Schistosoma spp.). |
 |
| Fig 46. A, Schistosoma mansoni egg. B, Schistosoma haematobium egg.C, Schistosoma japonicum egg, unstained wet mounts. |
 |
| Fig 47. Diagram of a tapeworm. |
 |
| Fig 48. Life cycle of Diphyllobothrium latum. |
 |
| Fig 49. Diphyllobothrium latum egg. |
 |
| Fig 50. Life cycle of Taenia spp. |
 |
| Fig 51. Taenia sp. ovum, unstained wet mount. |
 |
| Fig 52. Life cycle of Hymenolepis spp. |
 |
| Fig 53. Hymenolepis nana egg. |
 |
| Fig 54. Hymenolepis diminuta egg. |
 |
| Fig 55. Dipylidium caninum egg packet. |
 |
| Fig 56. Life cycle of Enterobius vermicularis. |
 |
| Fig 57. Enterobius vermicularis egg. |
 |
| Fig 58. Trichuris trichiura egg. |
 |
| Fig 59. Life cycle of Ascaris lumbricoides. |
 |
| Fig 60. Ascaris lumbricoides egg, fertile |
 |
| Fig 61. Life cycle of hookworm. |
 |
| Fig 62. Hookworm egg. |
 |
| Fig 63.
A, Hookworm rhabditiform larva. Notice long buccal capsule and lack of prominent genital primordium. B, Hookworm rhabditiform larva, buccal capsule. |
 |
| Fig 64. Life cycle of Strongyloides stercoralis. |
 |
| Fig 65. A, Strongyloides stercoralis rhabditiform larva, buccal capsule.B, S. stercoralis rhabditiform larva. Notice short buccal capsule and prominent genital primordium. |
 |
| Fig 66. Trichinella spiralis larva (biopsy specimen). |
 |
| Fig 67. Generalized life cycle of microfilaria. |
 |
| Fig 68. Wuchereria bancrofti microfilaria. Notice faintly staining sheath extending from both ends of organism. |
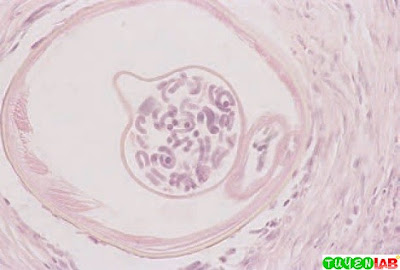 |
| Fig 69.
Cross-section of tissue infected with Onchocerca volvulus. |
This is only a part of the book : Textbook of Diagnostic Microbiology 4th edition 2011 of authors: Connie R. Mahon, Donald C. Lehman and George Manuselis. If you want to view the full content of the book and support author. Please buy it here: https://goo.gl/IawVC1










COMMENTS